Contemporary companies no longer operate on one platform. CRMs are used by sales teams, automation tools by marketers, accounting software by finance, and ticketing systems by support. When these tools fail to communicate with one another, the teams are wasting time, and the data is becoming useless.
That’s where the integration of CRM becomes essential. An integrated CRM transforms fragmented solutions into an interconnected ecosystem that operates silently in the background and keeps teams in check and customers happy.
This article deconstructs the process of integrating CRM with other tools, why it is important, and how to integrate it without causing havoc.
What Is CRM Integration?
It is important to be clear before getting down to tactics.
CRM Integration Meaning
CRM integration is the process of linking your customer relationship management system to other business tools so that the data flows automatically between the systems. Information is automatically updated in real time or on a schedule as opposed to manual updates.
CRM Integration Definition (In Simple Terms)
A CRM integration is a technical configuration that enables your CRM to exchange data with other systems, such as email systems, accounting software, or helpdesk software.
If you’re asking what a CRM integration is, think of it as a bridge. Data no longer has to be copied and pasted by human beings, but crosses the bridge.
Why the Integration of CRM Matters More Than Ever?
Lacking interconnected tools brings about unseen issues. Sales are out of context, support is out of history, and marketing is working off old lists.
Through CRM integration, businesses will benefit:
- One source of customer truth.
- More efficient processes and fewer mistakes.
- Increased interdepartmental visibility.
- Better relationships with customers.
Teams cease to seek information and begin to do something about it.
Tools that are usually used with CRM Systems
Most CRM systems relate to dozens, even hundreds, of tools. The trick here is to select integrations that can facilitate actual workflows.
CRM Integration to Marketing Tools
Sales decisions are powered by marketing data.
Popular integrations are:
- Email marketing platforms
- Marketing automation tools
- Social media management software.
These integrations are in sync with leads, campaign activity, and engagement scoresino the CRM. The sales reps will be able to view the clicks, oopens or conversions without tab switching.
Integration With Sales Tools CRM
The productivity of sales is time and context-dependent.
Examples of common sales integrations are:
- Email and calendar apps
- Proposal and contract tools
- Dialers and call tracking programs.
With CRM integration tools in place, emails are logged automatically, meetings update records, and deals move faster through the pipeline.
CRM Integration with Customer Support Systems
Customer loyalty is determined by support interactions.
Integrations with:
- Helpdesk software
- Live chat tools
- Chatbots
Enable support staff to view customer history in real time. There is also an insight into open tickets by sales teams before closing deals.
CRM Integration to Finance and Accounting Software
The customer picture is made complete with revenue data.
CRMs are integrated with accounting integrations to:
- Invoicing tools
- Subscription billing solutions.
- Payment gateways
This arrangement minimizes billing mistakes and provides finance departments with superior visibility into forecasting.
Methods for CRM Integration
The effort to integrate is not always the same. The selection of the appropriate approach avoids unnecessary complexity.
Native CRM Integrations
Many CRMs have built-in integrations with other tools.
Best for:
- Quick setup
- Minimal technical work
- Standard workflows
Limitations:
- Less customization
- Limited logic options
Native integrations are effective in common cases but might not address edge cases.
Third-Party CRM Integration Tools
Systems can be connected via platforms such as Zapier or Make.
Why businesses use them:
- No-code or low-code setup
- Flexible workflows
- Faster experimentation
They are best suited to teams that do not require engineering resources to be automated. But complicated data logic may be more difficult to scale.
Custom API Integrations
Custom integrations involve APIs that are used to interconnect systems.
Best suited for:
- Complex workflows
- High data volumes
- Exceptional business needs.
This solution is fully controllable and needs development skills and maintenance.
Integrating CRM with other tools: Step-by-Step
Integration is best done in a planned manner. In a hurry to do it, broken workflows are a common occurrence.
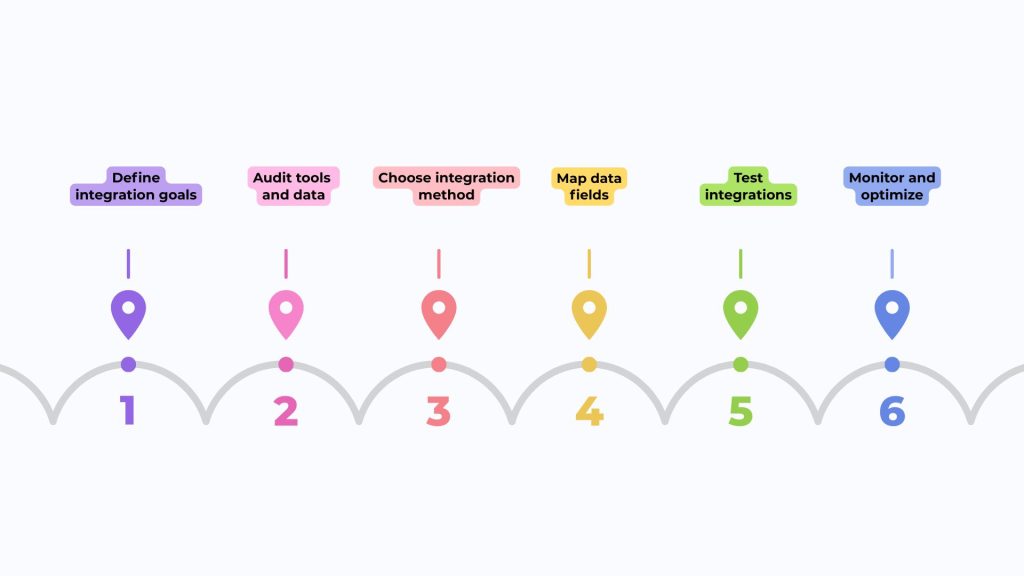
Step 1: Set Specific Integration Objectives
Begin with results, not implementations.
Ask:
- What data should be synced?
- Who uses it and when?
- Which manual processes should be automated?
Specific objectives discourage needless integration.
Step 2: Existing Tools and Data Audit
Identify all the tools dealing with customer data. Determine overlaps and inconsistencies.
This action usually exposes redundant systems or features that can be eliminated.
Step 3: Select the appropriate method of integration
Select the technique that fits your requirements:
- Native integration is to be fast.
- Flexibility through third-party tools.
- Custom advanced workflow APIs.
Simple use cases should not be overengineered.
Step 4: Map Data Fields Scrupulously
Data mapping determines the location of data.
Ensure:
- Field names match logically
- The needed fields are synchronized.
- Ownership rules are clear.
Duplicates and broken reports occur as a result of poor mapping.
Step 5: Before Full Deployment Test
Integrations should always be tested in a sandbox or limited environment.
Check:
- Data accuracy
- Sync frequency
- Error handling
Solve problems in time to prevent downtime.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize
Integration is not a single exercise.
Track logs, audit performance, and optimize business processes as the business requirements change.
Best Practices of CRM Integration Success
It has been proven that little decisions can go a long way.
Keep Data Clean
Every integration is enhanced by clean data.
- Standardize formats
- Remove duplicates
- Validate required fields
Integrations enhance the quality of data, good or bad.
Avoid Over-Integration
Increased integrations do not necessarily imply improved workflows.
Integrate only those tools that support:
- Revenue growth
- Customer experience
- Operational efficiency
Excessive connections are a nightmare in terms of maintenance.
Place more emphasis on Security and Compliance
CRM integrations deal with sensitive customer information.
Ensure:
- Secure authentication
- Permission controls
- Regulatory compliance.
Vulnerabilities destroy confidence in a short time.
Typical CRM Integration Problems (And Resolutions)
Even fixed arrangements come to a halt.
Data Duplication
Happens when records are made by several tools.
Fix: Establish a single system of record and impose ownership regulations.
Sync Failures
Data flow can be disrupted by API limits or network problems.
Fix: Monitoring alerts and retries.
Tool Compatibility Issues
None of the toolsintegratese well.
Fix: Test edge cases and compatibility before rollout.
CRM Integration Use Cases in the Real World
The importance of CRM integration is demonstrated by practical examples.
CRM + Email Marketing
Qualified leads are automatically forced into CRM pipelines through marketing campaigns. Sales make follow-up when the interest is new.
CRM + Support Platform
Customer profiles are updated with support tickets. Sales do not use upsells when issues are still unresolved.
CRM + Accounting Software
Closed deals create invoices immediately. Manual reconciliation work is reduced by finance teams.
CRM Integration Success Measurement
Measures determine the value of integration.
Track:
- Time saved on manual tasks
- Reduction in data errors
- Faster sales cycles
- Better customer satisfaction.
In case metrics do not improve, optimize workflows.
Trends in CRM Integration in the Future
CRM ecosystems keep changing.
Emerging trends include:
- Workflow automation through AI.
- Integration platforms that are low-code.
- Single customer data platforms.
The integration of CRM is shifting from a technical necessity to a strategic advantage.
Conclusion
A CRM in itself does not create growth. It is powerful because of its ability to relate well with the rest of your stack.
When carefully considered, CRM integration eliminates friction, enhances teamwork, and provides teams with a sense of clarity to act with certainty.
When your CRM is lonely, then it is time to reconsider the relationships behind it.
FAQs
1. What is CRM integration?
CRM integration links your CRM to other tools and allows automatic sharing of data, enhanced workflows, and uniformity of customer information across systems.
2. Why is the integration of CRM important for businesses?
The integration of CRM reduces manual work, prevents data silos, improves team efficiency, and creates a unified customer experience.
3. What are common CRM integration tools?
Common CRM integration tools include native CRM connectors, automation platforms like Zapier, and custom API-based integrations.
4. What are the tools that can be incorporated into a CRM system?
CRM systems are combined with marketing systems, sales systems, customer support systems, accounting systems, and analytics systems.
5. What is the average time of CRM integration?
CRM integration times range between hours in case of native integrations to weeks in case of complex custom API-based integrations.

